작성이유
- JS Error는 무엇이 있을까..? Error 핸들링에 대한 궁금증 해소
- 매번 중복되는 try-catch 코드
- React ErrorBoundary에 대해서 궁금하다.
TL;DR
- Exception vs Error
- Exception
- 프로그램에서 발생한다
- 복구 할 수 있다 (에러 핸들링!)
- Error
- 시스템의 자원이 부족해서 발생(Overflow, OutofMemory)
- 복구 할 수 없다.
- Exception
- JS 정의된 Error는 총 7개의 에러가 있다.(InternalError 에러제외)
- ReferenceError : 사용할 값이 없거나, 아직 초기화 안될 경우
- SyntaxError : 문법적인 오류(Parsing 중에 Error 발생)
- TypeError : 기본형, 참조형 Type의 Method가 없거나, 잘못 사용할 경우(const인데, 재할당)
- Try-catch는 SyntaxError, PromiseError는 에러 핸들링하지 못한다.
- React 16부터는 에러를 선언전으로 관리하기 위해 ErrorBoundary를 사용
- static getDerivedStateFromError
- componentDidCatch
JS Error
1. Error vs Exception
- Error
- 프로램에서 발생하지 않으며 시스템의 자원이 부족해서 발생
- 복구 할 수 없다(outofmemory)
- 다른 언어에서는 Unchecked Type이라고 정의
- StackOverflowError
- OutofMemoryError
- IOError
- Exception
- 작성한 프로그램에서 발생(에러가 발생하여 Flow가 멈춘다)
- 복구 할 수 있다(try-catch… Error handling)
- 다른 언어에서는 Checked, Unchecked Type 정의
- Checked - SQLException, IOException
- UnChecked - CalssCastException, NullPointException
2. JS Error Type
-
정의 : 런타임 환경에서 에러 오브젝트를 Throw
-
커스텀 Exception을 정의하여 에러로 사용할 수 있다
new Error('Custom Error')
-
-
EvalError
- eval() 발생하는것이나, 현재 ECMAScript에서는 더 이상 thrown 되지 않는다.
- 하위 버전 지원을 남아져 있다.
-
RangeError
- 허용되는 값의 집합(argument로 올수 있는 값) 또는 범위에 있지 않을때 오류 발생
new Array(-1) // RangeError: Invalid array length String().normalize(NaN) // RangeError: The normalization form should be one of NFC, NFD, NFKC, NFKD. Number().toExponential(101) // RangeError: toExponential() argument must be between 0 and 100 Number().toFixed(101) // RangeError: toFixed() digits argument must be between 0 and 100 Number().toPrecision(101) // RangeError: toPrecision() argument must be between 1 and 100 -
ReferenceError
- 사용할 변수의 값이 아직 초기화가 안되거나, 없을경우
console.log(foo) // ReferenceError: foo is not defined const foo = [1]- 하지만 우리의
var는 그런게 없다.. 함수형 스코프이기 때문에 호이스팅…
console.log(foo) // undefined var foo = [1] // or foo = [1] (var 키워드 없음)- 위 코드에서 TDZ가 발생하지 않는 경우? 전역 스코프이기 때문에 const, let은 block 스코프이다
{ console.log(foo) // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'foo' before initialization const foo = [1] } -
SyntaxError
- 잘못된 문법(토큰 순서 등)으로 인해 code parsing중에 발생(JS언어 컴파일러 - 인터프리터)
- 자바스크립트는 친절해서 Error가 발생한 위치까지도 알려준다.
break function () { } // SyntaxError: Unexpected keyword 'function'. (1:6) le foo = 1; // SyntaxError: Missing semicolon. (1:2) -
TypeError
- 값이 가지고 있는 타입대로 사용하지 않을때 발생
const foo = 1 foo = 2 // TypeError: Assignment to constant variable. const obj = {} obj() // TypeError: obj is not a function Object.unknownProp.method() // TypeError: Cannot read properties of undefined (reading 'method') -
URIError
- 유효하지 않는 문자가 포함된 문자열을 encode/decode 발생
decodeURIComponent('%') // URIError: URI malformed encodeURI('\uD800') '�' // URIError: URI malformed encodeURI('\uD800\uDFFF') '' // error 발생하지 않음 // 위 유니코드는 두개의 쌍으로 이루어져 있는데 하이-로우 쌍의 쌍 중 하나가 누락되서 에러 -
AggregteError
- 여러 오류를 하나의 오류로 표현하기 위해 사용
Promise.any([Promise.reject('1')]) // Uncaught (in promise) AggregateError: All promises were rejected
3. 에러 핸들링(Try-Catch)
-
try-catch, try-catch-finally
-
try 문에서 exception이 throw되면 catch블록이 실행 되면서 error 객체를 받아온다
try { throw new Error('oops') } catch (ex) { console.error('outer', ex.message) } // "outer" "oops" -
finally 블록에서 return이 되면 해당 try-catch-finally statement의 try-catch 에서 어떠한 값이 return이 되더라도 그 값으로 리턴된다
;(function () { try { try { throw new Error('oops') } catch (ex) { console.error('inner', ex.message) throw ex } finally { console.log('finally') return } } catch (ex) { console.error('outer', ex.message) } })() // Output: // "inner" "oops" // "finally"
-
-
JS Error를 막아보자!!!!
-
RangeError, ReferenceError, TypeError, URIError는 try-catch 핸들링 가능!
function foo() { try { // RangeError new Array(-1) String().normalize(NaN) // ReferenceError console.log(foo) const foo = [1] // TypeError Object.unknownProp.method() // URIError decodeURIComponent('%') } catch (err) { return 'catch the exception' } } foo() // 'catch the exception' -
Syntax Error와 Aggregte Error는 그대로 에러 노출
-
Syntax Error는 parsing 단계에서 에러가 발생하는거라서 try-catch문을 실행시키지 못한다
-
-
Promise 에러는 Promise 의 catch method로 자체적으로 처리하기 때문에, 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
-
암묵적으로 try -catch 블록으로 쌓여져 있다라고 생각하면 된다.
-
then 메소드 뒤에 있는 catch 메소드가 앞에 있는 Error를 핸들링 할 수 있다.
-
catch method 뒤에 있는 then 메소드로 추가적인 flow를 이어 갈 수 있다.
function foo() { new Promise((resolve, reject) => { throw new Error('에러 발생!') }) .catch(function (error) { console.log( '에러가 잘 처리되었습니다. 정상적으로 실행이 이어집니다.' ) }) .then(() => console.log('다음 핸들러가 실행됩니다.')) } foo()
-
-
- async - await에서는 에러가 어떻게 잡힐까?
- await 키워드를 사용하면 Promise의 result값을 반환한다.
- Error 라면 throw Error를 호출한것과 동일하므로 try-catch로 잡을 수 있다.
4. try - catch를 중복적으로 사용할때가 있다 공통화 처리 할 수 없을까?
-
try block 안에서 함수가 실행되어야 catch가 잡을 수 있다.
function wrappingLog(fn) { return (...args) => { try { return fn(...args) } catch (err) { console.log(err) } } } function foo() { throw new Error(2) } function bar() { throw new Error(1) } wrappingLog(foo)() wrappingLog(bar)()
리엑트에서 에러 관리는 어떻게 할까?(React ErrorBoundary)
1. 정의
- react 16에서 에러를 선언적으로 처리하기 위해 ErrorBoundary라는 개념을 도입
- try - catch 처럼 에러가 발생한다면 catch 에서 값을 리턴하는 것처럼 fallback UI를 노출
- 컴포넌트에서 에러가 발생한다면, 빈화면이나, 에러 로그를 출력(별 다른 조치를 취할 수 없었다)
2. ErrorBoundary에서 처리할 수 없는 에러
- 이벤트 핸들러
- 비동기적 코드 (예:
setTimeout혹은requestAnimationFrame콜백) - 서버 사이드 렌더링
- 자식에서가 아닌 에러 경계 자체에서 발생하는 에러
3. ErrorBoundary 관련 Method
-
Class Component만 해당 Method로 구현되어 있으면, 함수형으로 사용하지 못한다.
static getDerivedStateFromError - 렌더단계에서 발생 - 렌더링 결과로 수집한 내용으로 Virtual DOM을 생성하고 이전 Virtual DOM과 비교하는 단계까지를 말한다. componentDidCatch - Commit 단계에서 발생 - 렌더단계의 결과물인 Virtual DOM을 이용해 계산된 모든 변경사항 실제 DOM에 적용하는 단계를 말한다.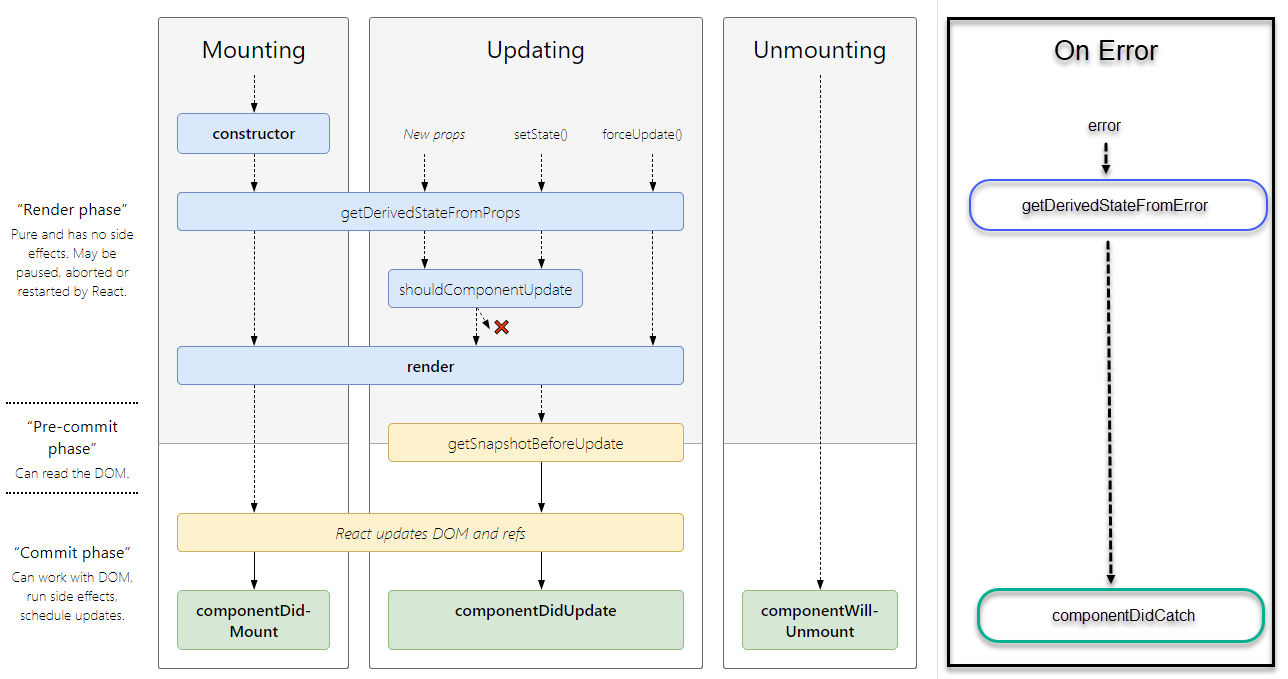
4. Custom ErrorBoundary
-
Reset Method를 통해 ErrorBounary안에서 컴포넌트를 다시 Recovery 할 수 잇음
-
상위 State가 변하니까, 하위 컴포넌트가 다시 렌더링..
interface Props { children?: ReactNode fallback: React.ElementType } interface State { hasError: boolean info: Error | null } class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component<Props, State> { public state: State = {hasError: false, info: null}; static getDerivedStateFromError(error: Error): State { return {hasError: true, info: error}; } componentDidCatch(error: Error) { // send error to Server(like sentry) } reset = () => { this.setState({hasError: false, info: null}) } render() { const { children } = this.props const { hasError, info } = this.state if (this.state.hasError) { return <this.props.fallback reset={this.reset} error={info} /> } return children; } } function ErrorCard({error, reset}: { error: Error, reset: () => void }) { return <div>Error <button onClick={reset}>reset</button></div> } function App() { return ( <ErrorBoundary fallback={(error, reset) => <ErrorCard error={error} reset={reset}/>}> <Foo/> // throws Error </ErrorBoundary> ); }
-
5. 에러의 종류가 다르다.. 에러를 나눠서 관리하자 → 에러 바운더리를 하나더 만들자
-
한곳에서 에러를 관리한다면 좋다
-
하지만 layer를 나누면 에러를 구분하기에 더 좋지 않을까?
class ErrorBoundary extends CommonErrorBoundary { constructor(props: Props) { super(props) } render() { const { children } = this.props const { hasError, info } = this.state if (info?.message === GlobalError) { throw new Error(info) // 상위 에러 바운더리로 호출 } if (this.state.hasError) { return <this.props.fallback reset={this.reset} /> } return children } } class GlobalErrorBoundary extends CommonErrorBoundary { constructor(props: Props) { super(props) } render() { const { children } = this.props if (this.state.hasError) { return <div>This is global Error</div> } return children } } ;<GlobalErrorBound> <ErrorBoundary fallback={ErrorCard}> <Foo /> </ErrorBoundary> </GlobalErrorBound>
출처
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_M7pUHfpaxk&ab_channel=LearnCoding
- https://pediaa.com/what-is-the-difference-between-error-and-exception-in-c/
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6115896/understanding-checked-vs-unchecked-exceptions-in-java
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Error
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Promise/catch
- https://ko.javascript.info/promise-error-handling
- https://ko.reactjs.org/docs/error-boundaries.html
- https://tecoble.techcourse.co.kr/post/2021-10-01-react-query-error-handling/
- https://fe-developers.kakaoent.com/2022/221110-error-boundary/