TL;DR
리엑트의 특징을 가지는 Component- 단일책임원칙 - 한가지의 기능/역할을 가진다
의미있는 테스트를 할 정도의 Component- UI라면, Ul 기준
- 기능이라면, 기능 기준
0. 글을 작성하는 이유?
- Q. 컴포넌트는 어떤 단위로 작성되는게 좋을까?
- A. 테스트를 할 정도의 크기라는 답변을 받았다.
- 의미있는 테스트를 할 정도의 크기 -> UI / 기능
- 리엑트 컴포넌트의 특징을 가지는 컴포넌트 단위(재사용)
1. 리엑트의 특징
- Declarative
- Component-Based
1) Imperative vs Declarative (명령형 vs 선언형)
- 예제
// 식당
명령형: 12번 테이블이 비어 있습니다. 나는 저 자리로 걸어가서 않을 겁니다.
선언형: 1명이요!
// 대리운전
명령형: 주차장 북쪽출구로 나와 좌회전. 12번가 출구가 나올 때까지 I-15 North를 타십시오.
이케아에 가듯이 출구에서 우회전하세요. 직진하여 첫 번째 신호등에서 우회전하십시오.
다음 신호등을 지나 계속해서 다음 신호등에서 좌회전하세요. 내 집은 # 298입니다
선언형: 내 주소는 ㅇㅇ 아파트입니다- Declarative 같은 경우, Imperative 방식(구현)이 추상화 된것을 알 수있다.
- 식당 : 식당의 직원은 빈 자리를 찾아 인원수에 맞는 자리를 안내할것
- 대링운전: 해당 목적이를 GPS or 경험을 통해 갈것
- Declarative을 수행/사용하기 위해서는 먼저 Imperative이 구성되어 있어야한다.
- 단, 어떻게 구현되었는지, 작동하는지 모를뿐이다
- Code Base 예제
- 명령형
function double(arr) {
let results = []
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
results.push(arr[i] * 2)
}
return results
}
function add(arr) {
let result = 0
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
result += arr[i]
}
return result
}
$('#btn').click(function () {
$(this).toggleClass('highlight')
$(this).text() === 'Add Highlight'
? $(this).text('Remove Highlight')
: $(this).text('Add Highlight')
})- 선언형
function double(arr) {
return arr.map((item) => item * 2)
}
function add(arr) {
return arr.reduce((prev, current) => prev + current, 0)
}
;<Btn
onToggleHighlight={this.handleToggleHighlight}
highlight={this.state.highlight}
>
{this.state.buttonText}
</Btn>- Declarative을 통해 코드는 더 읽기 쉬어졌다
- map/ruduce가 어떻게 동작하는지 모른다
- react가 state가 변경되면 어떻게 UI를 바꿔줄지는 모른다.
- Declarative 프로그래밍의 또 다른 장정은 프로그램의 컨텍스트가 독립적이라는 것이다.
- 명령형 같은 경우 현재 프로그램의 컨텍스트를 의존하는 경우가 많기 때문이다.
- 함수형 프로그랭이 선언적 프로그래밍의 하위집합니다.
2) Component?
- 프로그래밍
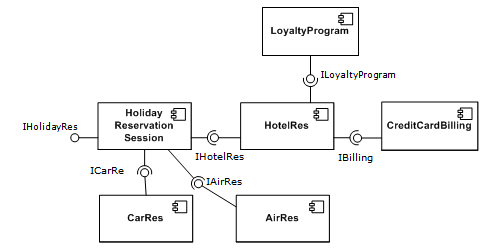
- 하나 이상 함수를 모아 하나의 특정한 기능을 수행하는 작은 기능적 단위를 말한다.
- 특징은 응집도는 높게 결합도를 낮게 → 관심사 분리를 강조 (종속 X, 재사용/교체가 가능)
- 컴포넌트는 제공된 인터페이스를 통해 사용될뿐, 어떻게 작동/구현되는지 알 필요가 없다(캡슐화)
- 이러한 컴포넌트를 활용한 프로그래밍 방법론을 CBSE / CBD (Component-based software engineering / component-based development)라고 부른다.
- React
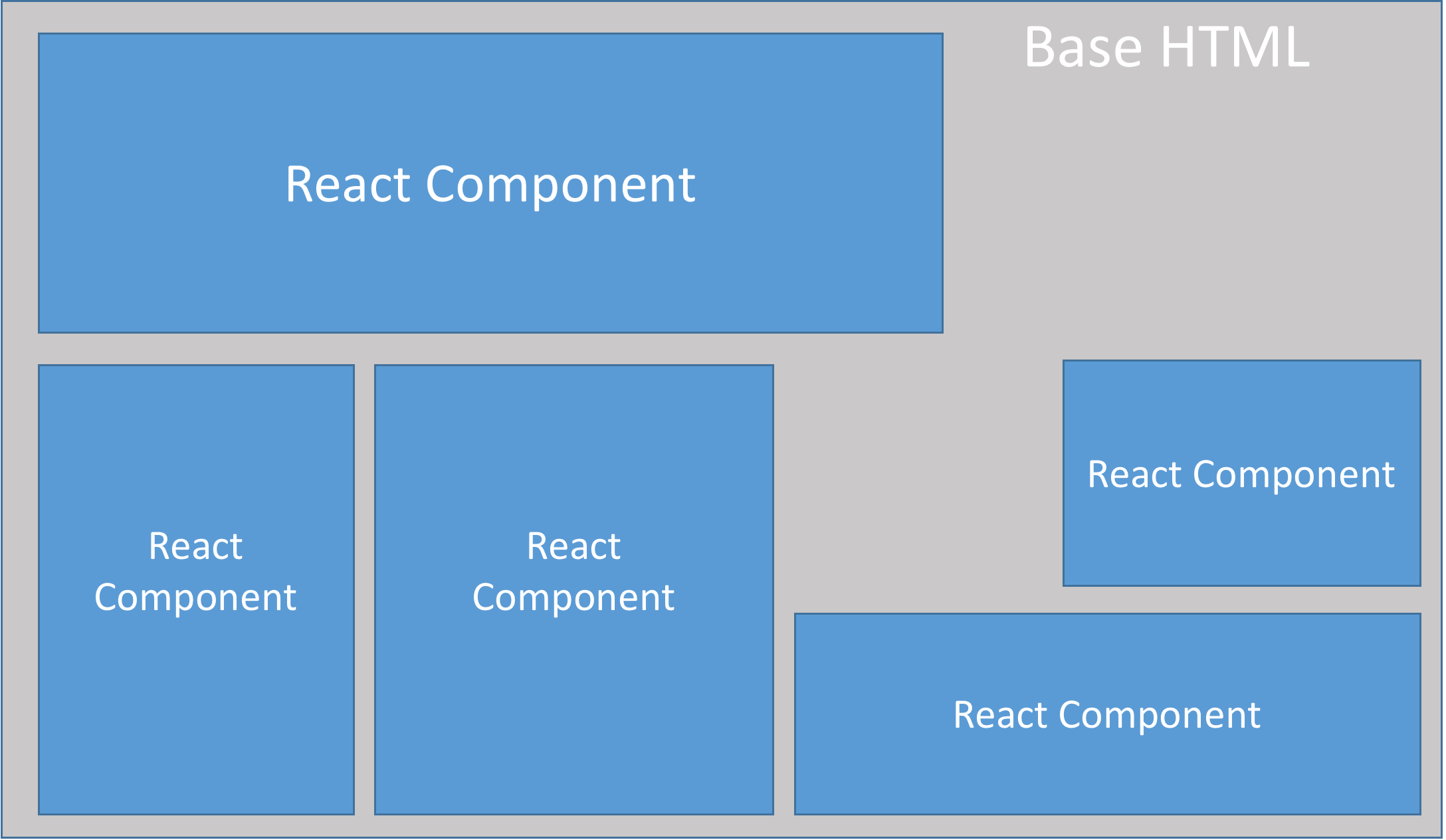
- 컴포넌트란 독립적이며, 재활용가능한 코드의 조각 ⇒ Component - Based
- 응집도는 높게 결합도를 낮게 → 관심사 분리를 강조 (종속 X, 재사용/교체가 가능)
- 컴포넌트는 제공된 인터페이스를 통해 사용될뿐, 어떻게 작동/구현되는지 알 필요가 없다(캡슐화)
- State, Props를 사용하여 UI를 보여준다.
- 상태가 변경되면, 해당 UI도 변경된다.
- 자바스크립트의 함수 역할이 동일하지만, JSX(HTML)를 리턴한다.
2. Test를 통해 컴포넌트 단위를 생각해보자
- 컴포넌트를 테스트하는 이유
- 확장 가능성 있는 코드 작성 및 코드의 질을 올리기 위해
- 리펙토링을 했는데 기존 기능이 정상 작동하는지 확인하기 위해
- 컴포넌트 크기를 조절하기 위해 → 의미있는 Test를 할 정도
- CRA는 기본적으로 React Testing Library 를 지원하며, 이를 활용해 UI Test를 진행한다.
- data-testId를 통해 DOM에 접근하여 테스트를 진행한다 하지만 이러한 test 속성이 production 코드를 들어가는걸 방지하기 위해 바벨 플러그인을 제공한다
- cypress 같은 경우 React Testing Library 처럼 data-cy 속성을 사용 (링크)

function ProductCategoryRow({ category }: ProductCategoryRowProps) {
return (
<tr>
<th colSpan={2}>{category}</th>
</tr>
)
}
function ProductRow({ product }: ProductRowProps) {
const name = product.stocked ? (
product.name
) : (
<span style={{ color: 'red' }} data-testid="stocked-element">
{product.name}
</span>
)
return (
<tr>
<td>{name}</td>
<td>{product.price}</td>
</tr>
)
}
function ProductTable({
products,
filterText,
inStockOnly,
}: ProductTableProps) {
const rows: ReactNode[] = []
let lastCategory: string
products.forEach((product) => {
if (product.name.indexOf(filterText) === -1) {
return
}
if (inStockOnly && !product.stocked) {
return
}
if (product.category !== lastCategory) {
rows.push(
<ProductCategoryRow
category={product.category}
key={product.category}
/>
)
}
rows.push(<ProductRow product={product} key={product.name} />)
lastCategory = product.category
})
return (
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Price</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>{rows}</tbody>
</table>
)
}
function FilterableProductTable() {
const [filterText, setFilterText] = useState('')
const [inStockOnly, setInStockOnly] = useState(false)
return (
<div>
<ProductTable
products={PRODUCTS}
filterText={filterText}
inStockOnly={inStockOnly}
/>
</div>
)
}
describe('fullTest', () => {
test('ProductTable', () => {
render(
<ProductTable
products={PRODUCTS}
filterText={''}
inStockOnly={false}
/>
)
const category = screen.getByText(PRODUCTS[0].category)
expect(category).toBeInTheDocument()
})
test('ProductRow', () => {
const product = PRODUCTS[0]
render(<ProductRow product={product} />)
const price = screen.getByText(product.price)
expect(price).toBeInTheDocument()
})
test('StockedProductRow', () => {
const stockedProduct = PRODUCTS[2]
render(<ProductRow product={stockedProduct} />)
const stockElement = screen.getByTestId('stocked-element')
expect(stockElement).toBeInTheDocument()
})
test('ProductCategoryRow', () => {
const category = PRODUCTS[0].category
render(<ProductCategoryRow category={category} />)
const element = screen.getByText(category)
expect(element).toBeInTheDocument()
})
})3. API, CustomHook, Redux Test 방법
-
api 관련 테스트(msw을 활용 - Mock API)
// msw/index.ts import {rest} from 'msw' import {setupServer} from 'msw/node' const server = setupServer( rest.get('/greeting', (req, res, ctx) => { return res(ctx.json({greeting: 'hello there'})) }) ) export default server // index.tsx const initialState = { error: null, greeting: null, } function greetingReducer(state: typeof initialState , action: any) { switch (action.type) { case 'SUCCESS': { return { error: null, greeting: action.greeting, } } case 'ERROR': { return { error: action.error, greeting: null, } } default: { return state } } } type Props = { url: string } export default function Fetch({url}: Props) { const [{error, greeting}, dispatch] = useReducer( greetingReducer, initialState, ) const [buttonClicked, setButtonClicked] = useState(false) const fetchGreeting = async (url: string) => axios .get(url) .then(response => { const {data} = response const {greeting} = data dispatch({type: 'SUCCESS', greeting}) setButtonClicked(true) }) .catch(error => { dispatch({type: 'ERROR', error}) }) const buttonText = buttonClicked ? 'Ok' : 'Load Greeting' return ( <div> <button onClick={() => fetchGreeting(url)} disabled={buttonClicked}> {buttonText} </button> {greeting && <h1>{greeting}</h1>} {error && <p role="alert">Oops, failed to fetch!</p>} </div> ) } // index.test.tsx beforeAll(() => server.listen()) afterEach(() => server.resetHandlers()) afterAll(() => server.close()) test('loads and displays greeting', async () => { render(<Fetch url="/greeting" />) fireEvent.click(screen.getByText('Load Greeting')) await waitFor(() => screen.getByRole('heading')) expect(screen.getByRole('heading')).toHaveTextContent('hello there') expect(screen.getByRole('button')).toBeDisabled() }) test('handles server error', async () => { server.use( rest.get('/greeting', (req, res, ctx) => { return res(ctx.status(500)) }), ) render(<Fetch url="/greeting" />) fireEvent.click(screen.getByText('Load Greeting')) await waitFor(() => screen.getByRole('alert')) expect(screen.getByRole('alert')).toHaveTextContent('Oops, failed to fetch!') expect(screen.getByRole('button')).not.toBeDisabled() }) -
CustomHooks Test
// usePage.ts const usePage = (url: string) => { const [data, setData] = useState('') const [isLoading, setLoading] = useState(true) useEffect(() => { axios .get(url) .then((response) => { const { data } = response const { greeting } = data setLoading((prev) => !prev) console.log({ isLoading }) setData(greeting) }) .catch((error) => { console.log('erroe') setLoading(false) setData(error) }) }, []) return [data, isLoading] } // usePage.test.ts const setupRenderCustomHook = () => { return renderHook(({ url }) => usePage(url), { initialProps: { url: '/greeting', }, }) } describe('usePage', () => { it('usePage를 새로운 pageId와 호출하면 isLoading은 true이다.', async () => { const { result, waitForNextUpdate, rerender } = setupRenderCustomHook() await waitForNextUpdate() const [data1, isLoading2] = result.current console.log(result.current) rerender() const [data, isLoading] = result.current console.log({ data1, isLoading2, data, isLoading }) expect(data).toBe('hello there') expect(isLoading).not.toBe(true) rerender() expect(isLoading).not.toBe(true) }) }) -
Store Test
// store/index.ts export const initialState = [ { text: 'Use Redux', completed: false, id: 0, }, ] const todosSlice = createSlice({ name: 'todos', initialState, reducers: { todoAdded(state, action: PayloadAction<string>) { state.push({ id: state.reduce( (maxId, todo) => Math.max(todo.id, maxId), -1 ) + 1, completed: false, text: action.payload, }) }, }, }) // store/index.test.ts test('should return the initial state', () => { const foo = reducer(undefined, {}) console.log(foo) expect(foo).toEqual([ { text: 'Use Redux', completed: false, id: 0, }, ]) }) test('should handle a todo being added to an empty list', () => { const previousState: typeof initialState = [] expect(reducer(previousState, todoAdded('Run the tests'))).toEqual([ { text: 'Run the tests', completed: false, id: 0, }, ]) }) test('should handle a todo being added to an existing list', () => { const previousState = [ { text: 'Run the tests', completed: true, id: 0, }, ] expect(reducer(previousState, todoAdded('Use Redux'))).toEqual([ { text: 'Run the tests', completed: true, id: 0, }, { text: 'Use Redux', completed: false, id: 1, }, ]) })